Multiple Linear Regression Example
Multiple Linear Regression Example
- Dataset
- Import Libraries
- Read and Preprocessing Data
- Train Model
- Predict
- Visualize results of the model
- Backward Elimination
- Re-build Model
- Re-predict
- Visualize the results
- Results
Bu yazıda, hava durumu, sıcaklık, rüzgar durumu gibi değişkenler kullanarak nem (humidity) seviyesini tahmin etmeyi amaçladığımız bir çoklu doğrusal regresyon çalışmasını ele alacağız.
Dataset
Import Libraries
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sbn
Read and Preprocessing Data
Read Data
data = pd.read_csv('tennis.csv')
print(data.head(15))
outlook temperature humidity windy play
0 sunny 85 85 False no
1 sunny 80 90 True no
2 overcast 83 86 False yes
3 rainy 70 96 False yes
4 rainy 68 80 False yes
5 rainy 65 70 True no
6 overcast 64 65 True yes
7 sunny 72 95 False no
8 sunny 69 70 False yes
9 rainy 75 80 False yes
10 sunny 75 70 True yes
11 overcast 72 90 True yes
12 overcast 81 75 False yes
13 rainy 71 91 True no
Analysis of Data
sbn.pairplot(data) # for better visualization
print(data.describe())
temperature humidity
count 14.000000 14.000000
mean 73.571429 81.642857
std 6.571667 10.285218
min 64.000000 65.000000
25% 69.250000 71.250000
50% 72.000000 82.500000
75% 78.750000 90.000000
max 85.000000 96.000000
Split Data
outlook = data.iloc[:, 0:1].values
temperature = data.iloc[:, 1:2].values
humidity = data.iloc[:, 2:3].values
wind = data.iloc[:, 3:4].values
play = data.iloc[:, 4:5].values
Encoding
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder, OneHotEncoder
le = LabelEncoder()
ohe = OneHotEncoder()
outlook = ohe.fit_transform(outlook).toarray()
wind = le.fit_transform(wind).reshape(-1, 1)
play = le.fit_transform(play).reshape(-1, 1)
Concatenate data
last_data = np.concatenate([outlook, temperature, humidity, wind, play], axis=1)
# Convert to DataFrame from numpy array
last_data = pd.DataFrame(data= last_data, columns=['overcast', 'rainy', 'sunny', 'temperature', 'humidity', 'windy', 'play'])
print(last_data.head(15))
overcast rainy sunny temperature humidity windy play
0 0.0 0.0 1.0 85.0 85.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 1.0 80.0 90.0 1.0 0.0
2 1.0 0.0 0.0 83.0 86.0 0.0 1.0
3 0.0 1.0 0.0 70.0 96.0 0.0 1.0
4 0.0 1.0 0.0 68.0 80.0 0.0 1.0
5 0.0 1.0 0.0 65.0 70.0 1.0 0.0
6 1.0 0.0 0.0 64.0 65.0 1.0 1.0
7 0.0 0.0 1.0 72.0 95.0 0.0 0.0
8 0.0 0.0 1.0 69.0 70.0 0.0 1.0
9 0.0 1.0 0.0 75.0 80.0 0.0 1.0
10 0.0 0.0 1.0 75.0 70.0 1.0 1.0
11 1.0 0.0 0.0 72.0 90.0 1.0 1.0
12 1.0 0.0 0.0 81.0 75.0 0.0 1.0
13 0.0 1.0 0.0 71.0 91.0 1.0 0.0
Train Test Split
xbağımsız değişkeni; overcast, rainy, sunny, temperature, windy, playybağımlı değişkeni; humidty
olacak şekilde verisetini ayırıyorum.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x = last_data.iloc[:, 0:7].values
x = pd.DataFrame(x)
x = x.drop(4, axis=1)
y = last_data.iloc[:, 4].values
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.33, random_state=0)
Train Model
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(x_train, y_train)
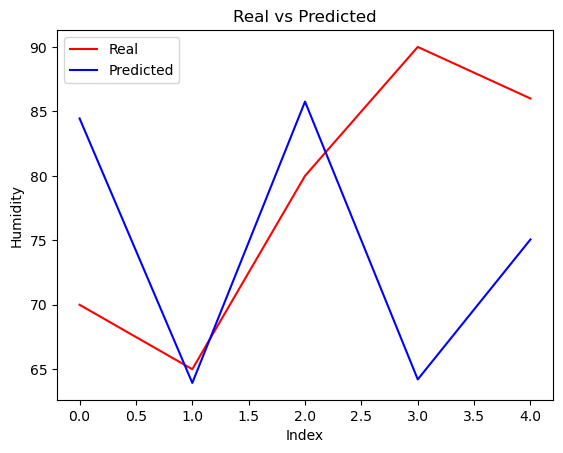
Predict
y_pred = lr.predict(x_test)
for i in range(len(y_pred)):
print('Predicted: ', y_pred[i], '\tReal: ', y_test[i])
Predicted: 84.45365572826714 Real: 70.0
Predicted: 63.938399539435814 Real: 65.0
Predicted: 85.76050662061026 Real: 80.0
Predicted: 64.21013241220496 Real: 90.0
Predicted: 75.06793321819228 Real: 86.0
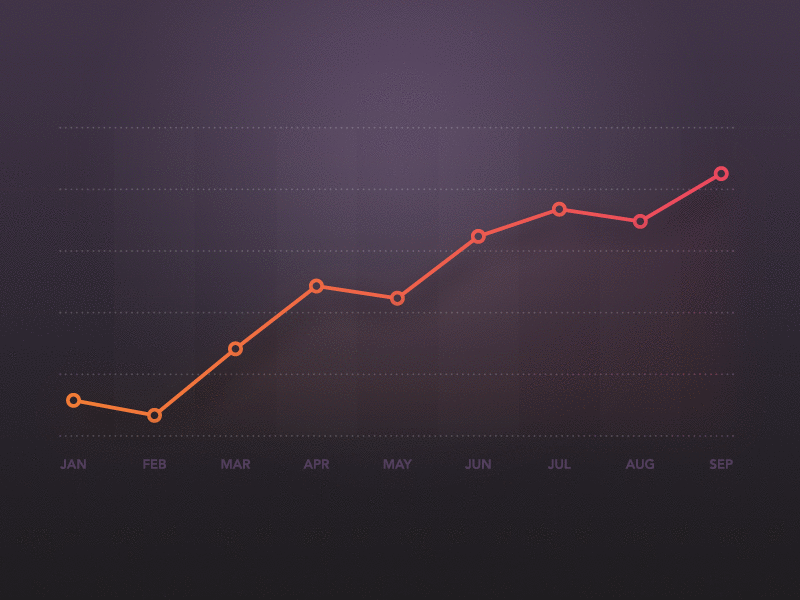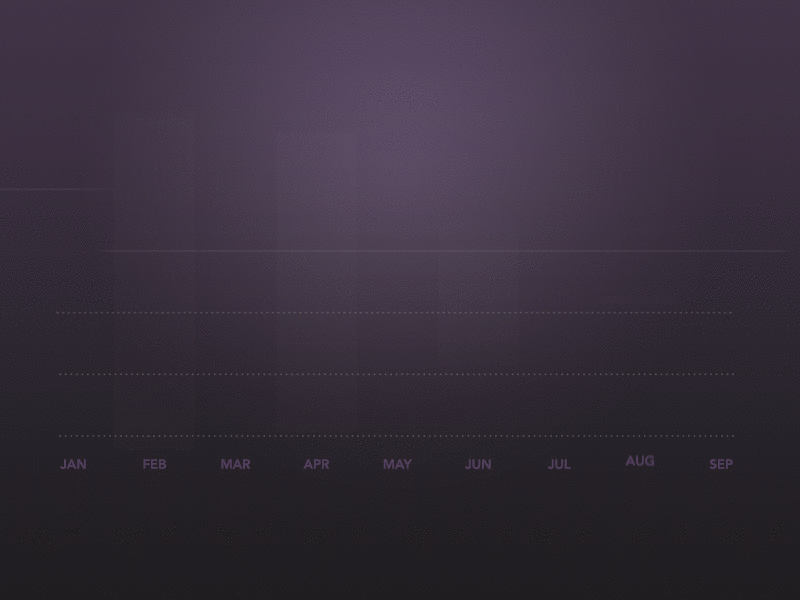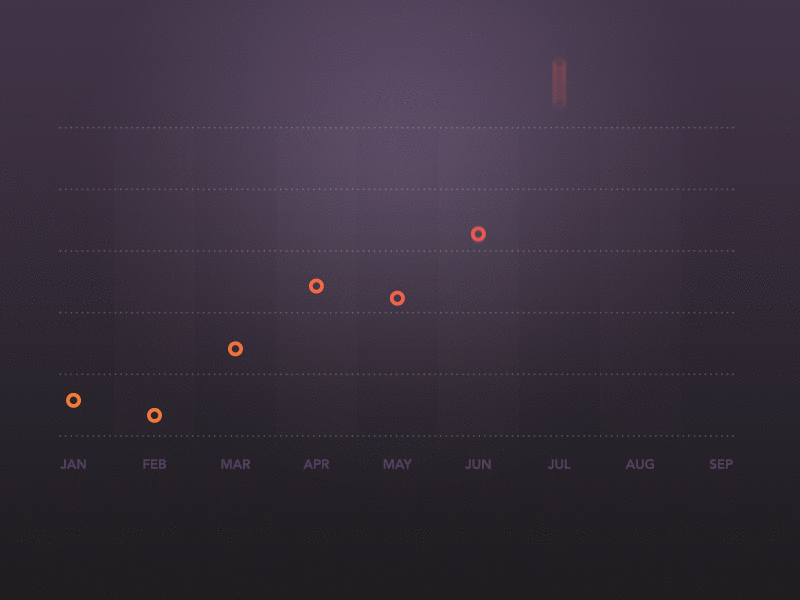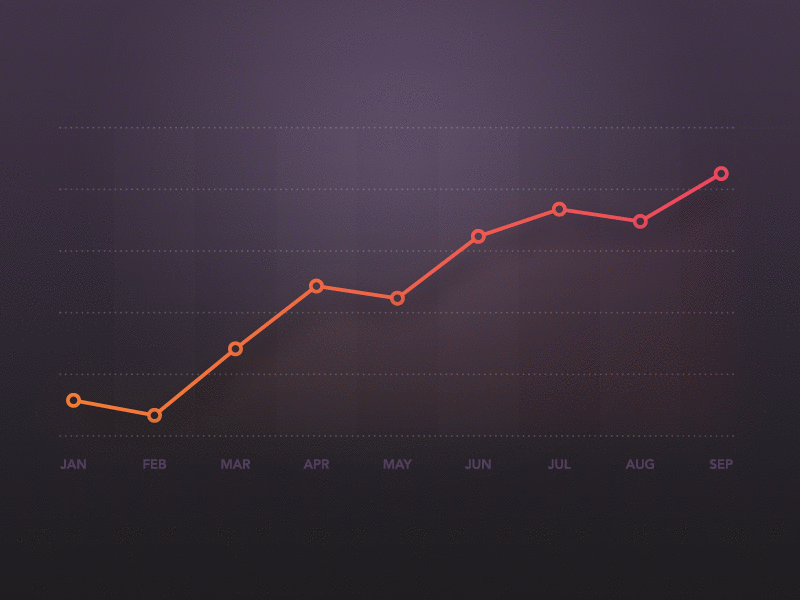
Visualize results of the model
plt.plot(y_test, color='red', label='Real')
plt.plot(y_pred, color='blue', label='Predicted')
plt.title('Real vs Predicted')
plt.xlabel('Index')
plt.ylabel('Humidity')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Backward Elimination
Adding constant
constant = np.ones((len(x), 1)).astype(int)
x = np.append(arr=constant, values=x, axis=1)
Backward Elimination
import statsmodels.api as sm
x_opt = x[:, [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]]
model = sm.OLS(endog=y, exog=x_opt).fit()
print(model.summary())
OLS Regression Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: y R-squared: 0.294
Model: OLS Adj. R-squared: -0.148
Method: Least Squares F-statistic: 0.6653
Date: Tue, 06 Aug 2024 Prob (F-statistic): 0.661
Time: 19:03:32 Log-Likelihood: -49.542
No. Observations: 14 AIC: 111.1
Df Residuals: 8 BIC: 114.9
Df Model: 5
Covariance Type: nonrobust
==============================================================================
coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const 39.3630 35.781 1.100 0.303 -43.149 121.875
x1 13.0261 15.032 0.867 0.411 -21.637 47.689
x2 16.2707 10.134 1.605 0.147 -7.099 39.641
x3 10.0661 13.179 0.764 0.467 -20.325 40.457
x4 0.4920 0.597 0.825 0.433 -0.884 1.868
x5 -4.0286 7.229 -0.557 0.593 -20.698 12.641
x6 -8.2778 8.029 -1.031 0.333 -26.793 10.237
==============================================================================
Omnibus: 0.935 Durbin-Watson: 2.416
Prob(Omnibus): 0.627 Jarque-Bera (JB): 0.823
Skew: 0.389 Prob(JB): 0.663
Eliminate x5
x_opt = x_opt[:, [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6]]
model = sm.OLS(endog=y, exog=x_opt).fit()
print(model.summary())
OLS Regression Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: y R-squared: 0.266
Model: OLS Adj. R-squared: -0.060
Method: Least Squares F-statistic: 0.8165
Date: Wed, 07 Aug 2024 Prob (F-statistic): 0.546
Time: 00:04:08 Log-Likelihood: -49.809
No. Observations: 14 AIC: 109.6
Df Residuals: 9 BIC: 112.8
Df Model: 4
Covariance Type: nonrobust
==============================================================================
coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const 28.4191 28.743 0.989 0.349 -36.601 93.440
x1 8.2373 11.852 0.695 0.505 -18.573 35.047
x2 13.4944 8.481 1.591 0.146 -5.690 32.679
x3 6.6873 11.245 0.595 0.567 -18.750 32.125
x4 0.6484 0.506 1.282 0.232 -0.496 1.793
x5 -6.2865 6.909 -0.910 0.387 -21.916 9.343
==============================================================================
Omnibus: 0.887 Durbin-Watson: 2.360
Prob(Omnibus): 0.642 Jarque-Bera (JB): 0.810
Skew: 0.424 Prob(JB): 0.667
Kurtosis: 2.181 Cond. No. 8.20e+17
Re-build Model
x = x_opt
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.33, random_state=0)
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(x_train, y_train)
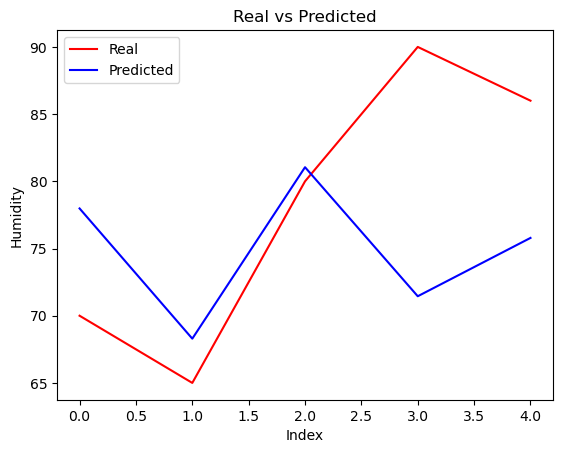
Re-predict
y_pred = lr.predict(x_test)
for i in range(len(y_pred)):
print('Predicted: ', y_pred[i], '\tReal: ', y_test[i])
Predicted: 77.98135141680795 Real: 70.0
Predicted: 68.29304916444661 Real: 65.0
Predicted: 81.05037539355777 Real: 80.0
Predicted: 71.44926132235409 Real: 90.0
Predicted: 75.78905303947685 Real: 86.0
Visualize the results
plt.plot(y_test, color='red', label='Real')
plt.plot(y_pred, color='blue', label='Predicted')
plt.title('Real vs Predicted')
plt.xlabel('Index')
plt.ylabel('Humidity')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Results
Bu çalışmada, hava durumu ve diğer çevresel değişkenleri kullanarak nem seviyesini tahmin eden bir çoklu doğrusal regresyon modeli geliştirdik ve değerlendirdik. Çoklu doğrusal regresyon modeli, nem tahmininde makul bir doğruluk sağlamıştır. Ayrıca, spor aktiviteleri gibi hava koşullarının kritik rol oynadığı alanlarda veri bilimi ve makine öğrenmesi uygulamalarının nasıl değer katabileceğini de ortaya koymaktadır.